|
Tycoon : buying and selling processor capacity in real-time.
Tycoon is an open source project launched in HP Labs Palo Alto, that enables the emergence of markets where CPU cycle delivery to a user automatically adapts to competition in demand.
To whom Tycoon can benefit?
Such a market-based resource allocation system should open the grid to business. However, the initial goal is as pragmatic as the reasons why money was invented: so that farmers don't eat only their own production.
Impact on the grid
Such a system is a necessary step towards Grid democratization. At present, a resource provider buys a server and decides to allow certain people or virtual organizations (VOs) to queue and run their jobs on it. Based on differences in the importance of users' missions, and on how many resources they are expected to need on average, each user is allocated once and for all a certain proportion of the whole CPU capacity.
The current exchange of resources is determined by static contracts between providers and users, based each time on explicit interests on both sides. With Tycoon, contracts are implicit and the exchange is made dynamic and seamless. As a consequence commercial companies will have a reason to provide resources and merge their intragrids into inter-grids; and foreign users will show up.
Providing resources
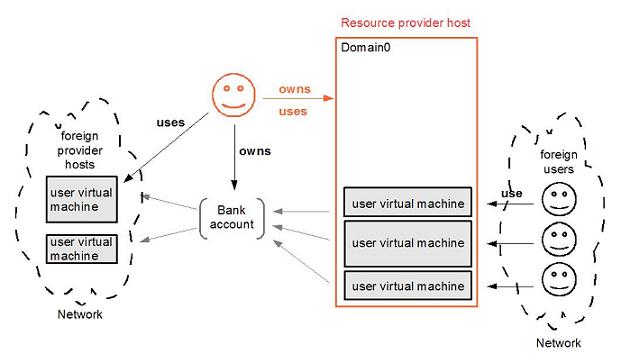
From the resource provider's point of view, there is no idle CPU time. Selling CPU capacity to the world via Tycoon means avoiding waste: When a CPU runs for other users, it generates money on the provider's Tycoon bank account. The provider can later spend this money on other servers when she needs more resources than she physically owns.
Currently academia buy servers and offer a proportion of their usage to each VO they want to support. Following the same idea, they can provide more flexible resources in opening a restricted Tycoon market (only for these particular VOs), or joining the internet-wide Tycoon market, and in both cases transfering earnings to the VOs' Tycoon bank accounts in the same proportion than they allocate CPU time now. All transactions can be made automatically and the system leads to a more optimal resources utilization with less accounting struggle.
Using resources
From the resource user's point of view, CPU cycles are available when needed. The user does not have to queue until a less urgent or less important job from another user / VO is terminated. If she values the job a lot, She can have it run accordingly by bidding more.
The Tycoon bidding system is made so that users have an incentive to match their bids to the real value they give to CPU speed on this machine, at a given time, relatively to the competition. Actually users do not have to bid themselves: they delegate this task to the Tycoon agent. The default agent uses the optimal algorithm for the choice of the machine. The user only has to modify his bidding rate on real time with a sliding bar, if necessary.
Openlab collaboration
The Tycoon team at HP labs Palo Alto already demonstrated the efficiency of their solution as a generic system. Openlab contributes by investigating the system's usability in the context of high energy physics research, and its coexistence with the mainstream grid middleware.
|
Pilot testing |
Tycoon is an emerging product. It has been presented to CERN in order to demonstrate its benefits on a large scale grid environment, targetting HEP physics users as an advanced research community with a high demand of resources. Openlab aims to anticipate this community's needs and test the system's behavior under realistic conditions, and then introduce Tycoon to HEP users and provide early support on site. It provides a number of dedicated HP servers for testing and providing resources. Openlab is also willing to launch large scale real-use experiment with other sites participating in pilot testing like Singapore National Grid Office (NGO) and Kurchatov Institute (Moscow) |
|
Resources virtualization |
Tycoon relies on Xen to virtualize resources: Tycoon lauches a virtual machine for each user who creates an account on a resource provider host. The user can then install her software and run her job. Our work on Tycoon leverages the significant effort made at openlab and by our partners in the domain of Xen virtualization. |
|
Integration into grid middleware |
Integration into the mainstream middleware is an important step for Tycoon to enter the production grid. Tycoon can already be used in ARC, the middleware stack used in NorduGrid, and openlab is discussing with EGEE and collaborating with the Greek Research and Technology Network for its integration in gLite. This integration would provide CERN users with higher level services to make the usage of Tycoon seemless. |
Resources
Tycoon Trac – HP labs Palo Alto Tycoon Wiki. Papers, sources, mailing lists, various information.
A video presentation – HP Labs scientist Kevin Lai and Prof. Bernardo Huberman present Tycoon.
|
